Fermentation. General information.
Under fermentation understand the set of sequential steps in making cooked and pre-heated to the desired temperature and the seed medium until completion of cell growth or the desired product biosynthesis. At the end of fermentation produced a complex mixture consisting of producer cells, not consumed nutrient solution and accumulated in the medium biosynthesis products. This mixture is referred to as culture liquid.
Depending on the purpose of production – getting the cells or their metabolic products – the main methods of fermentation vary. If the process is directed to the production of biomass, the fermentation purpose – to get the highest possible titer of the cell, and in case of accumulation of metabolites is carried out simultaneously with the formation of peaks and producing the desired product is always shifted in time. Therefore, the duration of the fermentation in the first case is always less than the second.
If the aim is to obtain biomass industrial strain in a batch process, the cultivation time of not more than 24 hours The production of primary metabolites biosynthesis time is 48-72 hours, and secondary -. 72-144 hours.
When culturing various microorganisms operating temperature range varies from 25-60 ° C, pH – 2.9, air flow in aerobic processes – 0,15-2,5 m3 / m3 medium 1 / min.
There are several ways to carry out the fermentation – periodic, semi-batch, continuous and polycyclic.
Batch process – a process such as the fermenter is fed seed material specific process parameters are set (temperature, pH, RPM agitator) and the process takes place independently from the desired product. This process is not economically advantageous because produced little of the desired product.
Semi-batch process is different from the batch process in that the fermentation in the fermentor are added various nutrients (sources of carbohydrate, nitrogen), adjusted pH during fermentation is added in a certain moment precursor fermentation. Semi-batch process is cost-effective, with high yield.
SUMMARY continuous process that from the fermenter during biosynthesis takes a certain amount of the culture broth and introduced into another fermenter, in which also begins biosynthesis. The culture fluid serves as inoculum. The fermenter, taken from which part of the culture liquid is added the same amount of water and it biosynthetic process continues. This operation is continuously repeated. Using the required number of fermenters and constantly shifting part of the culture liquid from one fermenter to the other is achieved by a closed cycle. The advantage of the continuous process is that step decreases the seed cultivation.
At the end of the fermentation process, 90% of polycyclic culture fluid is drained from the fermenter, and the rest serves as a seed.
Features of cultivation of animal cells.
Animal cells differ in many ways from prokaryotic and fungal cells: they grow slower, have great sensitivity to injury and the air bubbles. These properties influence the cell structure of bioreactors and fermentors, especially aeration and agitation systems, which, in use should not create stress conditions for culture.
Stirring should be homogeneous in order to avoid temperature gradients and pH, elevated concentrations of substrate and product. It is necessary to take into account the sensitivity of cells to injury. Typically mixing is carried out large paddle stirrer at low speed. Pneumatic (air) in airlift reactors mixing or stirring with hydraulic pumps in external reactors with suspended solid phase also solves the problems associated with the cultivation.
To prevent damage to the foam and the bubbles of air cells can reduce the amount of feed gas mixture used Bubble free surface aeration or venting through the membrane. By reducing the volume of the feed gas is necessary to increase its oxygen concentration. Optimum supply of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and air is created by mixing gas systems.
Cultivation of animal cells can be carried out in a stationary (batch), fixed the fed (fed- batch) or continuous (continuous) culture with or without retention of biomass. When stationary culturing cells grow without the addition of the substrate after sowing culture. However, the lack of substrate or formation of toxic metabolic products can reduce productivity. To avoid these problems apply to stationary culturing fed, wherein the substrate or other appropriate substance is added in portions or continuously. In the continuous cultivation of metabolic products which inhibit the growth – lactate, ammonia is removed by adding a compensating amount of fresh medium in order to avoid shortage of the substrate for growth.
Due to low productivity, slow growth related to animal cell culture process is preferably continuous with the detention cells (perfusion system). This leads to high cell density cultures and greater contact with their environment, which increases productivity. For biomass retention and prevent its removal with removable volumes of culture fluid using various filtration systems, for example, rotary or rotating filters.
To prevent damage to the foam and the bubbles of air cells can reduce the amount of feed gas mixture used Bubble free surface aeration or venting through the membrane. By reducing the volume of the feed gas is necessary to increase its oxygen concentration. Optimum supply of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and air is created by mixing gas systems. Cultivation of animal cells can be carried out in a stationary (batch), fixed the fed (fed- batch) or continuous (continuous) culture with or without retention of biomass. When stationary culturing cells grow without the addition of the substrate after sowing culture. However, the lack of substrate or formation of toxic metabolic products can reduce productivity. To avoid these problems apply to stationary culturing fed, wherein the substrate or other appropriate substance is added in portions or continuously. In the continuous cultivation of metabolic products which inhibit the growth – lactate, ammonia is removed by adding a compensating amount of fresh medium in order to avoid shortage of the substrate for growth. Due to low productivity, slow growth related to animal cell culture process is preferably continuous with the detention cells (perfusion system). This leads to high cell density cultures and greater contact with their environment, which increases productivity. For biomass retention and prevent its removal with removable volumes of culture fluid using various filtration systems, for example, rotary or rotating filters. Many mammalian cells grow only being attached to the surface. Such opornozavisimye immobilized cells on microcarriers, such as glass, cellulose, collagen, gelatin or plastic. If a porous support, the cells can grow therein, and they are protected from wound stress that allows higher speed stirring and purging during cultivation.
Analyzers Bioprofile FLEX when cultured animal cells.
Timely submission of the substrate in the fermenter, and you conclude metabolic products provide stable growth of culture and increase the efficiency of the cultivation process. Hardware complex of modern fermenetrov lets you control parameters such as the cultivation of the oxygen concentration, pH, temperature, but direct control indicators substrate concentration (eg, glucose) or metabolites (eg, lactate) is carried out additional methods and apparatus. The increasing prevalence for this task receive multi-parameter biochemical analyzers (Bioprofile FLEX), the measurement principle is based on biosensor technology. Such devices allow to measure several parameters from a single sample. one analysis time is 1-2 minutes. The analyzer can be integrated into the fermenter controller, the nutrient medium can be loaded on the analyzer readings.Thus, modern biotechnology analyzers (NOVA Bioprofile FLEX) can solve the problem of optimizing supply feeding into the fermenter and the withdrawal of metabolites from the fermentation medium, and, ultimately, to seek to increase the yield of the desired product.

Fig.1 Example of measurement results of the biochemical module of the Bioprofile FLEX.
Analyzer BioProfile FLEX combines the functionality of three off-line analyzers (biochemistry analyzer, the analyzer cell counting, osmometer) in a single device. The analyzer has a modular design, including gases modules / electrolytes, nutrients / metabolites, cell density / viability and osmometric module. Gas / electrolyte module and the module nutrients / metabolites using ion-selective electrodes, potentiometry, amperometry, and fermentation, depending on biosensors.
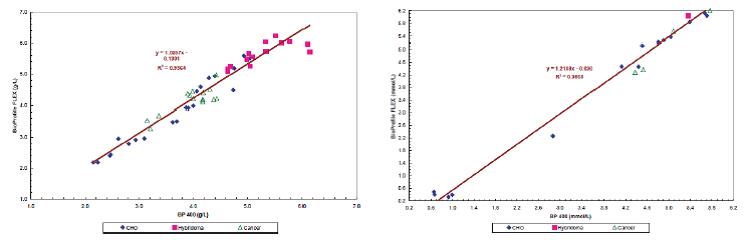
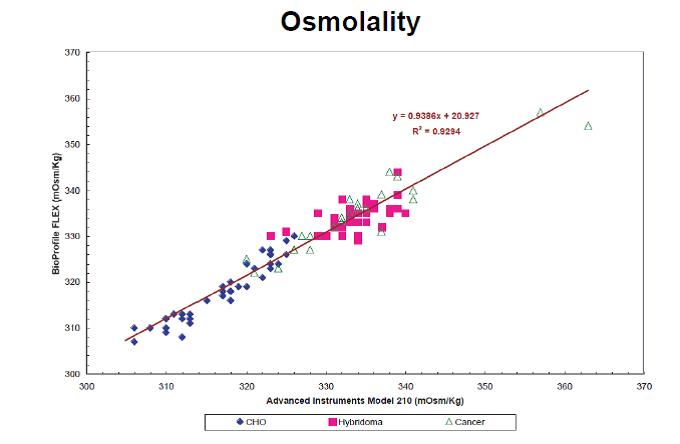
Fig.2 Example of measurement results of the modulus of osmometry Bioprofile FLEX.
Density module / cell viability was developed by Nova Biomedical for cell counting and viability assessment, based on the traditional tryptophan blue exclusion method. First, a sample of cells is mixed with tryptophan blue, and the mixture was incubated so that the dead cells absorb tryptophan blue. The sample is then deposited on the bottom of the translucent flowcell. The flow cell is moved to the fixed lens of the microscope with the help of high-precision motion control system, with high-resolution images. Cell counts and viability are determined by image processing based on user-defined constraints, such as the live / dead cells, the brightness and the average size of the cell.
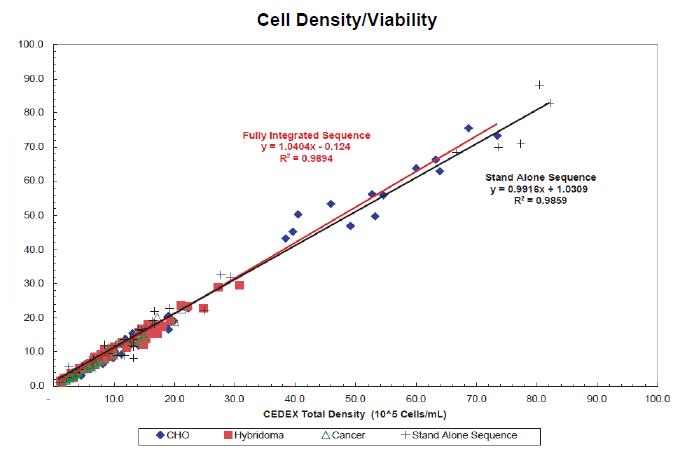
Fig.3 an Example of measurement results of module viability/cell density Bioprofile FLEX.

Each module can be selected individually, using all modules BioProfile FLEX require only 1 ml of the culture liquid sample and 7.5 min for performing analyzes. Results and user currently exported electronically in a spreadsheet format.
Although integrated analyzer with data entry part organizes the manual labor, but only a unique new automatic sampling system designed specifically to BioProfile Flex (NOVA Biomedical), allows you to completely eliminate the manual labor.
Numerous studies demonstrate the successful application of new integrated multi-analyzer and an automatic sampling system for monitoring of mammalian cell culture. The results indicate that the system has the potential to reduce the manual labor and associated errors. In this measurement process may take place in-line without interruption / disorders fermentation.